Storage Structure
- Main memory ( RAM )
- Programs must be loaded into RAM to run.
- Instructions and data fetched from RAM into registers.
- RAM is volatile
- "Medium" size and speed
- Other electronic ( volatile ) memory is faster, smaller, and more expensive per bit:
- Registers
- CPU Cache
- Non-volatile memory ( "permanent" storage ) is slower, larger, and less expensive per bit:
- Electronic disks
- Magnetic disks
- Optical disks
- Magnetic Tapes
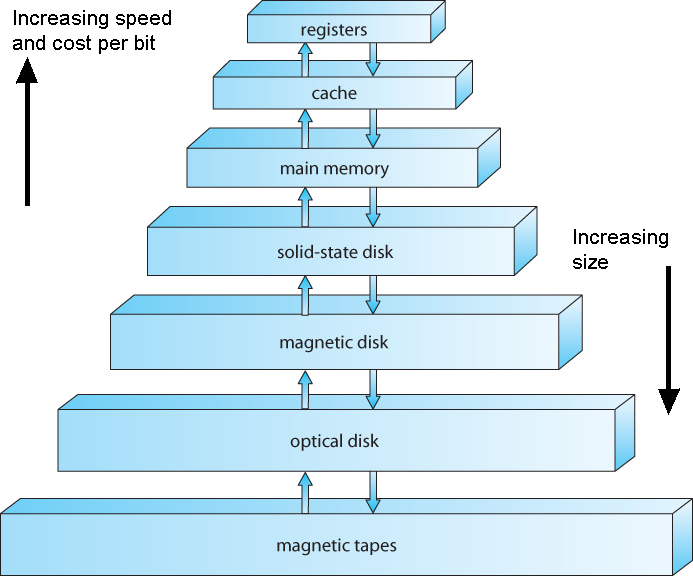
Figure 1.4 - Storage-device hierarchy
- Programs must be loaded into RAM to run.
- Instructions and data fetched from RAM into registers.
- RAM is volatile
- "Medium" size and speed
- Registers
- CPU Cache
- Electronic disks
- Magnetic disks
- Optical disks
- Magnetic Tapes
Figure 1.4 - Storage-device hierarchy